

Thyroid cancer - Radiofrequency - Puncture - Diagnosis - Treatment
Ablation of thyroid nodules by microwave

































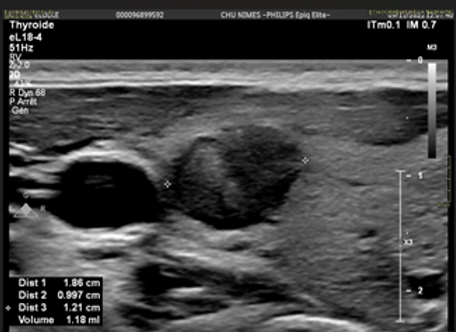









The ablation of thyroid nodules by microwave is a minimally invasive system that uses several applicators allowing the administration of a power (microwave) to tissue zones of 5 to 6 cm and the optimization of the duration of the treatment.
It is a hyperthermic procedure that aims to destroy the nodules through the application of electromagnetic energy and not an electric current.
Generation of an electromagnetic field with wavelengths between 0.03 and 30 cm and frequency between 900 and 2500 MHz to cause oscillation of polarized ions
Thermal spread is not as impeded by charring or heat loss as with RFA
Therefore, MWA offers the possibility of delivering more thermal electrical energy in a shorter or equivalent time which results in a higher final tissue temperature.
Some generator does not require a cooling system and there is no contraindication in case of pacemaker, metal prosthesis and pregnancy
The processing technique:
1-Local anesthesia:
Injection of xylocaine around the thyroid capsule
2- Hydrodissection
Hydrodissection is a technique that allows a safety zone between the nodule and the five critical structures (CVRGT) and to protect these structures (carotid, vagus nerve, recurrent nerve, middle sympathetic ganglion and tachylum).
Microwave treatment uses less power (20-30 Watts) than radiofrequency (40-50 Watts) which reduces the risk of complications and the use of hydrodissection.
3- trans-isthmic treatment
Microwave processing is based on multiple overlapping firing lines.
Trans-isthmic approach is recommended, which offers additional security and reduces complications, but some teams use the lateral approach.
The treatment is faster with the microwave with less power.
Visibility
The use of lower power minimizes the formation of "gas bubbles" and improves visibility of ablation progress under ultrasound guidance, giving good control to the operator when treating difficult lesions, thereby reducing the risk of potential damage to surrounding structures.
Applicators are designed to minimize energy loss.
Very Low Loss technology (VLLTM: Very Low Loss) allows the applicators to operate, in the absence of a cooling system, without causing skin burns.
Thyroid coils (18G x 8cm, and 17G x 10cm) are designed with a sturdy metal tip to also target calcified lesions, Teflon coated to ensure smooth penetration and positioning
The efficiency of the 17 G x 10 cm antenna is significantly superior in the volumetric reduction of nodules
Several studies performed to assess the long-term efficacy and safety of MWAs for the treatment of nodules.
The volumetric reduction varies according to the studies between 49.88 and 79.06%
The biological assessment remains normal
The disappearance of the cervical discomfort is gradual and the improvement noted one month after the treatment.
The indications for microwave ablation remain identical to radiofrequency:
1-Voluminous benign thyroid nodule on cytology twice, gradually increasing in volume with local discomfort.
2- a nodule responsible for biological or clinical hyperthyroidism
Clinical case 1
38-year-old patient with a thyroid nodule known since 2018 increased in volume (2.47cc), benign on cytology.
New cytopuncture under ultrasound guidance performed (October 2020) concluded benign nodule (BETHESDA 2)
June 2021
Increase in volume (3.24 cc) with the appearance of local discomfort,
New puncture: benign nodule
Proposal of microwave thermoablation due to progressive volumetric increase, appearance of discomfort and refusal of surgery.
New nodular volumetric augmentation before MW ablation with a volume of 4.27cc
2,47 cc 3, 24 cc 4,27 cc , i.e. a volumetric increase of 42.16%
Ultrasound control performed 3 months after thermal ablation by MW shows a volumetric reduction of 72.37%.
Clinical case 2
74-year-old patient with a thyroid nodule in the left lobe with ultrasound follow-up for more than 10 years, benign on cytology at 2-year intervals with progressive volumetric increase with local discomfort.
Microwave thermoablation
Nodular volume before treatment 13.6 cc (43.7 x 20.8 x 28.6 mm).
Microwave treatment with 17G antenna and 25W power
Nodular volume 3 months after microwave ablation 4.23 cc (23.1 x 17.7 x 19.8 mm), i.e. a volumetric reduction of 68.9% with disappearance of local discomfort.
Clinical case 3
43-year-old patient with biological hyperthyroidism (TSH = 0.04) with negative antibodies)
A scan shows a hot thyroid nodule.
An ultrasound performed shows a thyroid nodule of 4.81 cc (29.3 x 16 x 19.6 mm) with strong peripheral and central vascularization.
Ablation by microwave with a 17 G antenna and a power of 25 W.
The biological control 3 months after the treatment shows a normalization of the TSH to (1.57) and a nodular volume of 1.81 cc (22.2 x 10.6 x 14.7 mm) i.e. a reduction of 55.09% .




















